git 中文件一共有4种状态。 没有被跟踪的、没有修改的、已经修改的、已暂存的。
- 没有被跟踪的 -- 表示没有被纳入版本管理,通常临时文件或者编译的生成的文件,是没有被跟踪的状态。
- 没有修的 - 文件已经纳入的版本控制管理,并且已经提交到了版本系统。
- 已修改的 - 已提交的文件就是没有修的文件,修改后就变成了已修改状态 。
- 已暂存的 - 修改的文件提交前,需要放到暂存区(git add filename)。
四种状态的转变
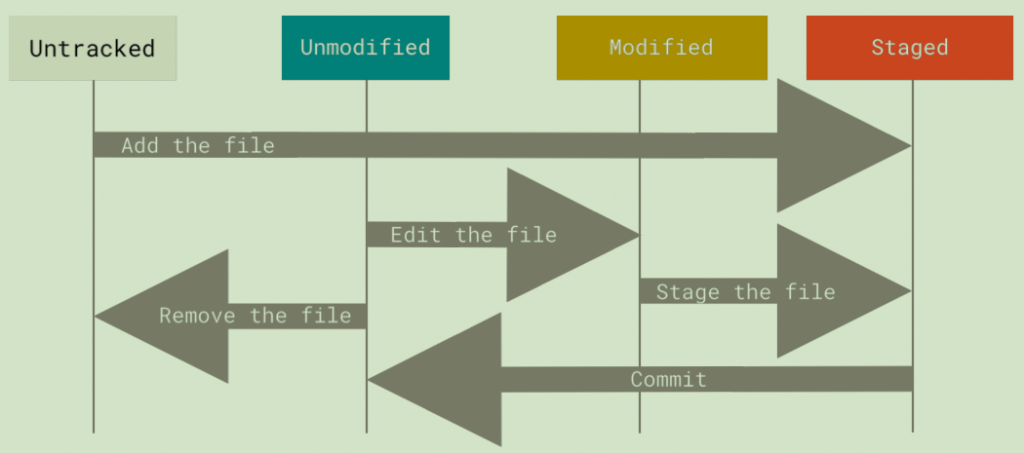
用文件 a.txt 作为演示
默认文件 a.txt 没有被跟踪,执行
mkdir -p ~/gittest
cd ~/gittest
git init .
echo "test" > a.txt
git add a.txt表示,文件已经暂存。可以在下次提交的时候,提交。查看当前的状态
git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: a.txt
提交 a.txt 文件
git commit -m 'submit a.txt'
[master (root-commit) e77a0f1] submit a.txt
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 a.txt
# 可以看到一个干净的目录
git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
修改 a.txt 文件
echo "test2" >> a.txt
# 查看状态
git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: a.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")查看已经跟踪的文件
git ls-tree -r master --name-only删除已跟踪的文件
git rm --cached a.txt
git commit -m 'delete a.txt'
git status
On branch master
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
a.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
可以看到文件 a.txt 没有被跟踪